If you’ve ever wondered whether you can build muscle, stay energized, or meet your daily protein needs without eating meat — the answer is absolutely yes.
High-protein vegetarian foods are not just tofu and beans. They’re part of a rich, diverse world of plant-based protein sources that deliver essential amino acids, fiber, and nutrients your body needs for strength, recovery, and long-term health.
This guide breaks down the best vegetarian protein options, explains the science behind their quality (like PDCAAS and amino acid completeness), and helps you plan meals that work for your goals — whether that’s fitness, weight management, or sustainable eating.
Table of Contents
What Makes a Food “High-Protein” for Vegetarians?
A high-protein vegetarian food contains at least 7–10 grams of protein per 100 grams and provides a good balance of essential amino acids.
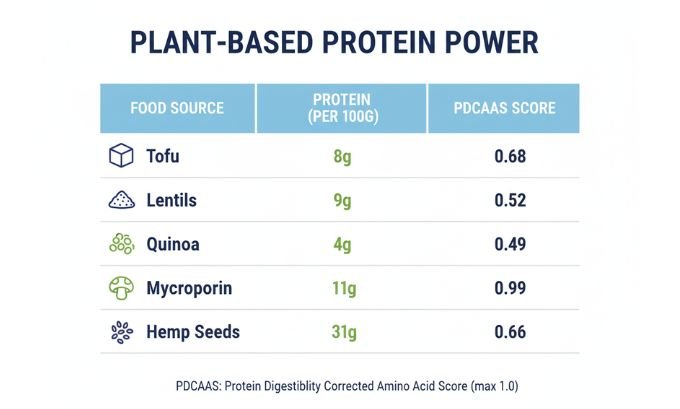
Protein isn’t just about quantity — quality matters too. The Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) measures how efficiently your body can use that protein. A score of 1.0 means the protein is highly digestible and complete (like soy protein or mycoprotein).
Key Concepts You Should Know
| Concept | Meaning | Why It Matters |
| Amino Acids | Building blocks of protein (9 are essential) | Needed for muscle repair and hormone balance |
| Complete Protein | Contains all 9 essential amino acids | Ensures balanced nutrition |
| PDCAAS | Measures protein digestibility & bioavailability | Higher score = higher quality |
| Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS) | The process of building new muscle tissue | Boosted by high-quality protein intake |
The Science Behind Plant-Based Protein
When people think “protein,” they often think meat or eggs. But plant-based protein — found in foods like legumes, soy, and grains — can be just as effective for muscle and metabolic health when eaten in the right combinations.
- Soy protein and mycoprotein (Quorn) are examples of complete proteins with PDCAAS close to 1.0.
- Legumes (like lentils and beans) and grains (like rice or oats) are incomplete individually, but when paired together, they form a balanced amino acid profile.
- Hemp seeds and quinoa sit in between — naturally rich and nearly complete, making them versatile staples for vegetarians.
If you’re looking to enhance your vegetarian diet with organic pantry staples in Japan, check out TokyoMart.store for nutrient-rich, high-protein options like lentils, quinoa, and hemp seeds.
Top High-Protein Vegetarian Foods (Ranked by Nutrition & Versatility)
1. Soy Protein: The Benchmark of Plant-Based Nutrition
Soy protein is the most complete and digestible plant-based protein, ideal for both muscle growth and general health.
Soy comes in many forms — tofu, tempeh, soy milk, edamame — and consistently tops the charts with a PDCAAS of 1.0, the same as egg or dairy protein.
Nutritional Snapshot (per 100g tofu):
- Protein: 8–10g
- Amino Acid Profile: Complete
- PDCAAS: 1.00
What’s Great About It:
- Excellent for muscle protein synthesis
- Contains BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids) similar to animal protein
- Versatile in both savory and sweet dishes
Considerations:
Some people prefer fermented soy (tempeh, miso) for better digestion. And while soy contains phytoestrogens, moderate intake is completely safe and backed by decades of nutritional research.
2. Legumes (Lentils, Chickpeas, Beans, Peas): The Everyday Protein Heroes
Legumes are the backbone of most vegetarian diets — affordable, filling, and protein-rich
Nutritional Snapshot (per 100g cooked lentils):
- Protein: 9g
- Fiber: 8g
- PDCAAS: 0.70
Why They Shine:
- Packed with lysine — an amino acid often missing in grains
- Promote heart and gut health due to fiber and antioxidants
- Easy to use in soups, curries, salads, and burgers
Balanced View:
Legumes are slightly lower in methionine (an amino acid), but when eaten with grains like quinoa or rice, they form a complete protein combination.
3. Mycoprotein (Quorn): The Future of Sustainable Protein
Mycoprotein is a high-quality, eco-friendly complete protein made from a type of edible fungi.
Nutritional Snapshot (per 100g Quorn mince):
- Protein: 11–12g
- PDCAAS: 0.99
- Fiber: 6g
Why It’s Impressive:
- Extremely digestible and rich in all essential amino acids
- Proven to support muscle protein synthesis after workouts
- Low in fat, high in satiety — perfect for weight management
Things to Note:
Some Quorn products include egg or milk ingredients, so vegans should check the label. Research also shows it has one of the lowest environmental footprints among protein sources.
4. Quinoa: The Complete Ancient Grain
Quinoa is one of the rare complete proteins in the plant kingdom, making it a great addition to vegetarian diets.
Nutritional Snapshot (per 100g cooked):
- Protein: 4g
- PDCAAS: 0.87
- Amino Acid Profile: Complete
Why It Works:
- Contains all essential amino acids including lysine and methionine
- Gluten-free and easily digestible
- Provides magnesium, iron, and antioxidants
Keep in Mind:
While quinoa is nutritious, its protein density is lower per serving compared to soy or legumes. Use it as a base grain in bowls or salads alongside higher-protein toppings.
5. Hemp Seeds: The Omega-Powered Protein
Hemp seeds are a functional food rich in plant-based protein and essential fatty acids.
Nutritional Snapshot (3 tbsp):
- Protein: 10g
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: 2g
- PDCAAS: 0.63
Why People Love Them:
- Nearly complete amino acid profile
- Excellent balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fats
- Anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for athlete
Practical Tips:
Add hemp seeds to smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, or salads for an instant protein boost. Combine with lentils or quinoa for better amino acid coverage.
How to Combine Vegetarian Proteins for Complete Nutrition
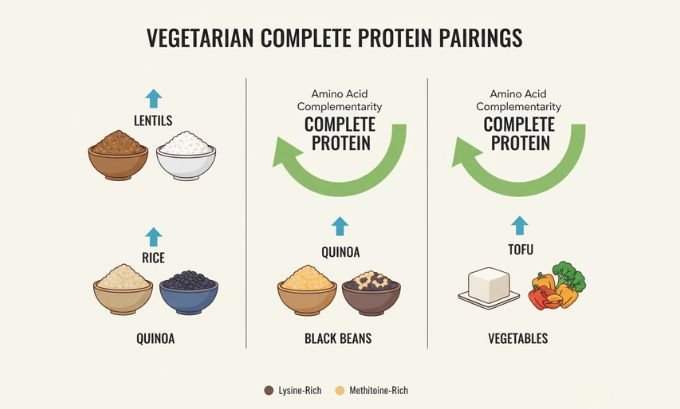
You can achieve complete protein coverage by mixing foods that complement each other’s amino acid gaps.
| Pairing | Example Meal | Benefit |
| Legumes + Grains | Lentil & rice bowl | Covers methionine & lysine |
| Soy + Vegetables | Tofu stir-fry | Naturally complete & rich in micronutrients |
| Hemp + Legumes | Hummus with hemp topping | Boosts omega-3s and amino acids |
| Quinoa + Beans | Quinoa chili | Doubles amino acid coverage |
Real-Life Example:
A lentil-quinoa bowl topped with hemp seeds offers complete protein, high fiber, and balanced fats — ideal for muscle recovery and satiety.
The Link Between Protein and Muscle Protein Synthesis
Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS) is how your body builds new muscle tissue — and it’s triggered by consuming enough high-quality protein.
- Studies show that soy protein and mycoprotein stimulate MPS nearly as effectively as whey protein when consumed in adequate amounts.
- For vegetarians, the key is to spread protein intake evenly across meals rather than eating most of it at once.
Practical Guideline:
Aim for 20–30 grams of protein per meal to maximize MPS, especially if you’re active or over 40 (as muscle efficiency decreases with age).
Strengths and Areas for Improvement
What’s Great About High-Protein Vegetarian Foods
- Environmentally sustainable and cruelty-free
- Often lower in saturated fats and cholesterol
- High in fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients
- Can support weight management and heart health
Challenges to Consider
- Some sources are incomplete proteins on their own
- May require higher volume or combination to meet protein targets
- Digestibility varies (improved through cooking, sprouting, or fermenting)
Sample 1-Day Vegetarian Protein Plan

| Meal | Protein Source | Approx. Protein (g) | Notes |
| Breakfast | Soy milk smoothie with hemp seeds | 20 | Fast-digesting protein & omega-3s |
| Lunch | Quinoa and lentil salad | 25 | Complete amino acid coverage |
| Snack | Mycoprotein wrap with veggies | 15 | High satiety & low fat |
| Dinner | Tofu stir-fry with brown rice | 30 | Balanced macro ratio |
| Total Daily Protein: | ≈90g | Ideal for active vegetarians |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can vegetarians get enough protein without supplements?
Yes. With foods like soy, lentils, quinoa, and mycoprotein, it’s easy to meet daily needs naturally.
2. What’s the best vegetarian protein for muscle gain?
Soy protein and mycoprotein are most effective due to their complete amino acid profile and high PDCAAS.
3. How much protein should I eat daily?
Most adults need 1.2–1.6g of protein per kilogram of body weight, or more if training intensely.
4. Is quinoa enough for complete protein intake?
Quinoa is complete, but it’s best used alongside legumes or soy for higher total protein density.
5. Are plant proteins harder to digest?
Some are, but cooking, fermenting, or soaking improves digestibility dramatically.
6. What’s the healthiest vegetarian protein snack?
Hummus with hemp seeds, edamame, or roasted chickpeas — high in protein and fiber.
Conclusion
High-protein vegetarian foods are no longer niche — they’re essential for modern, sustainable nutrition. By combining plant-based proteins like soy, legumes, quinoa, mycoprotein, and hemp seeds, you can easily achieve complete protein coverage while supporting your health and the planet.
Whether your goal is building muscle, managing weight, or simply eating better, a well-planned vegetarian diet provides all the amino acids and nutrients your body needs — naturally and deliciously.
Author Bio
Written by: Nutrition Research Collective
Reviewed by: Dr. Maya Allen, Ph.D. in Human Nutrition
With over a decade of research in plant-based diets, Dr. Allen specializes in protein metabolism and sustainable food systems.

